Cisco Crypto Key Generate Rsa Modulus 2048
- October 2, 2015
- Posted by: Syed Shujaat
- Category: Cisco, Networking Solutions
Crypto key generate rsa. cryptokeygeneratersa,page2 Cisco IOS Security Command Reference: Commands A to C, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches).
Use this command to generate RSA key pairs for your Cisco device (such as a router). keys are generated in pairs–one public RSA key and one private RSA key.
If your router already has RSA keys when you issue this command, you will be warned and prompted to replace the existing keys with new keys.
- The key pair generation command should possibly be done as “exportable” – for transferring the keys to another router later, if the need arises to replace the old box & etc. E.g.: crypto key generate rsa general-keys Label GDKey modulus 2048 exportable.
- Apr 03, 2015 First, create a key: crypto key generate rsa label mykey modulus 2048 Next, create a trustpoint which references the key, and generate a self-signed certificate: crypto ca trustpoint throwaway keypair mykey enrollment self crypto ca enroll throwaway noconfirm Now the throwaway trustpoint has a certificate. Export that certificate to the terminal.
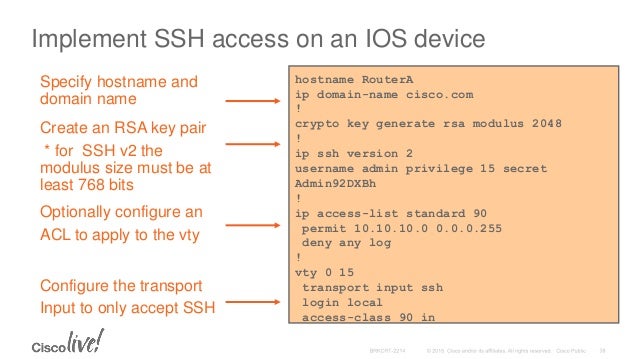
NOTE: Before issuing this command, ensure that your router has a hostname and IP domain name configured (with the hostname and ipdomain-name commands).
You will be unable to complete the cryptokeygeneratersacommand without a hostname and IP domain name. (This situation is not true when you generate only a named key pair.)
Here are the steps to Enable SSH and Crypto Key setup : 2 config must requried for SSH
1 Setup Local VTY line User ID and password
router (Config) # Line VTY 0 15
router (Config-line)# login local
router (Config-line)# Exit
!!! create local login ID/Pass
router (Config)# username [loginid] password [cisco]
router (Config)# username loginid1 password cisco1
2. router (Config)# ip domain-name example.com
router (Config)# crypto key generate rsa
how many bits in the modulus [512] :1024
router (Config)# ip ssh version2
Rsa key pair generator windows 7. router (Config)# CTRL Z
Note | Secure Shell (SSH) may generate an additional RSA key pair if you generate a key pair on a router having no RSA keys. The additional key pair is used only by SSH and will have a name such as {router_FQDN }.server. For example, if a router name is “router1.cisco.com,” the key name is “router1.cisco.com.server.” |
This command is not saved in the router configuration; however, the RSA keys generated by this command are saved in the private configuration in NVRAM (which is never displayed to the user or backed up to another device) the next time the configuration is written to NVRAM.

Modulus Length
When you generate RSA keys, you will be prompted to enter a modulus length. The longer the modulus, the stronger the security. However, a longer modules take longer to generate (see the table below for sample times) and takes longer to use.
The size of Key Modulus range from 360 to 2048. Choosing modulus greater than 512 will take longer time.
| Router | 360 bits | 512 bits | 1024 bits | 2048 bits (maximum) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco 2500 | 11 seconds | 20 seconds | 4 minutes, 38 seconds | More than 1 hour |
| Cisco 4700 | Less than 1 second | 1 second | 4 seconds | 50 seconds |
Cisco IOS software does not support a modulus greater than 4096 bits. A length of less than 512 bits is normally not recommended. In certain situations, the shorter modulus may not function properly with IKE, so we recommend using a minimum modulus of 2048 bits.
Syntax Description : Optional Strings to embed with SSH Crypto key
| general-keys | (Optional) Specifies that a general-purpose key pair will be generated, which is the default. | ||
| usage-keys | (Optional) Specifies that two RSA special-usage key pairs, one encryption pair and one signature pair, will be generated. | ||
| signature | (Optional) Specifies that the RSA public key generated will be a signature special usage key. | ||
| encryption | (Optional) Specifies that the RSA public key generated will be an encryption special usage key. | ||
| labelkey-label | (Optional) Specifies the name that is used for an RSA key pair when they are being exported.If a key label is not specified, the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the router is used. | ||
| exportable | (Optional) Specifies that the RSA key pair can be exported to another Cisco device, such as a router. | ||
| modulusmodulus-size | (Optional) Specifies the IP size of the key modulus.By default, the modulus of a certification authority (CA) key is 1024 bits. The recommended modulus for a CA key is 2048 bits. The range of a CA key modulus is from 350 to 4096 bits.
| ||
| storagedevicename: | (Optional) Specifies the key storage location. The name of the storage device is followed by a colon (:). | ||
| redundancy | (Optional) Specifies that the key should be synchronized to the standby CA. | ||
| ondevicename: | (Optional) Specifies that the RSA key pair will be created on the specified device, including a Universal Serial Bus (USB) token, local disk, or NVRAM. The name of the device is followed by a colon (:).Keys created on a USB token must be 2048 bits or less. |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| copy | Copies any file from a source to a destination, use the copy command in privileged EXEC mode. |
| cryptokeystorage | Sets the default storage location for RSA key pairs. |
| debugcryptoengine | Displays debug messages about crypto engines. |
| hostname | Specifies or modifies the hostname for the network server. |
| ipdomain-name | Defines a default domain name to complete unqualified hostnames (names without a dotted-decimal domain name). |
| showcryptokeymypubkeyrsa | Displays the RSA public keys of your router. |
| show crypto pki certificates | Displays information about your PKI certificate, certification authority, and any registration authority certificates. |
今日はSSHの設定方法を勉強します。
まだまだTelnet接続を使用している環境も多いと思いますが、世の中的にはManagementアクセスもよりセキュアにする方向に向かっているので、Telnetは割愛しました。
Catalystに192.168.1.1を設定し、SSHによるリモートアクセスを確認します。
IPの設定とインターフェースの開放
ログインUsernameとPasswordを作成し、vtyに設定。接続方法をSSHに限定。
ホスト名、ドメイン名の設定、RSA鍵の作成
SSHv2に限定
特権パスワードの設定
UsernameとPasswordはコンソール接続、リモート接続で共通のものをusername secretコマンドで設定します。passwordコマンドでも設定できますが、セキュリティ上username secretを使用することが推奨されます。この辺りは前回書きました。
http://qiita.com/jinnai73/items/a240bf2bc1325b46edfe
パスワードを作成したらlogin localコマンドでlineに適用します。Telnet接続を禁止するため、transport inputコマンドでsshでのログインのみ許可します。
続いてSSH接続に必要なRSA鍵を作成します。RSA鍵を確認するコマンドはshow crypto key mypubkey rsaです。
何も入っていませんね。鍵を生成するコマンドはcrypto key generate rsaですが、生成する前提としてスイッチのFQDN、つまりホストとドメイン名が決まっている必要があります。デフォルトではドメイン名が設定されていないため、以下のようなエラーが出ます。
ドメイン名の設定はip domain-nameコマンド、確認はshow hostsで行えます。
それではホスト名とドメイン名を設定しましょう。
Cisco Rsa Key
設定できました。これでRSA鍵も生成可能になります。crypto key generate rsaコマンドで生成、鍵長は2048 bitを指定します。
Cisco Switch Generate Rsa Key
警告メッセージにもある通り、2048 bitでは約1分ほど時間がかかりますが、2016年現在1024 bit以下のRSAは(少なくともインターネット上では)使わない方が良いというのは異論が無いところでしょう。
この時点でSSHでの接続が可能になります。テストのため自分自身に接続してみましょう。
できました。sshのv1はセキュリティに問題があるため禁止しましょう。一度ログアウトして、sshをv2に限定したのちに、v1での接続ができないことを確認します。
うまくできています。この状態ではSSHアクセスした後に特権モードに入ろうとしてもできないため、enable secretで特権パスワードの設定もしておきましょう。
思ったよりボリュームが増えてしまいました。明日ももう少し、機器管理を勉強しようと思います。